Science Meets Longevity
I’ve been asking the same question for a long time:
Why do we age, and can we fight it?
This site is my way of chasing the answers and sharing the tools, insights, and science I find along the way.

Journey Into the Biology of Time
I’ve been asking the same question for a long time:
Why do we age, and can we fight it?
This site is my way of chasing the answers and sharing the tools, insights, and science I find along the way.

Journey Into the Biology of Time
I’ve been asking the same question for a long time:
Why do we age, and can we fight it?
This site is my way of chasing the answers and sharing the tools, insights, and science I find along the way.

“The body doesn’t fall apart from silence, it unravels from noise.“
Welcome, listener to the body’s inner voices.
Aging is not just the story of individual parts wearing down. It is the gradual unraveling of the conversation that keeps the body whole. Muscles grow weaker, memory loses its sharpness, skin becomes thin, and the immune system grows unpredictable. Beneath these changes lies one of the most overlooked hallmarks of aging: altered intercellular communication.
Your body is like a vast city. Every cell is a home, a factory, or a watchtower, and the health of the city depends on the constant exchange of information. Cells speak in many languages: hormones, neurotransmitters, cytokines, and countless other molecular messages. In youth, these messages are precise and purposeful. But with time, the lines blur. Signals are delayed, distorted, or lost entirely. Some cells begin sending chaotic inflammatory messages that drown out the quiet instructions for repair and balance.
The connection between altered intercellular communication and aging runs through every organ system. It can disrupt immunity, cloud the brain, destabilize metabolism, and weaken the ability of tissues to coordinate their repair. In this breakdown of dialogue, the orchestra of the body begins to play out of tune.
In this exploration, we will uncover:
To understand altered intercellular communication and aging is to see how the loss of harmony between cells can ripple into the loss of harmony in the whole organism. Restoring that harmony may be one of the most profound ways to preserve health and vitality.
Let us tune our ear to the whispers and shouts within, and learn how to bring the conversation back into balance.
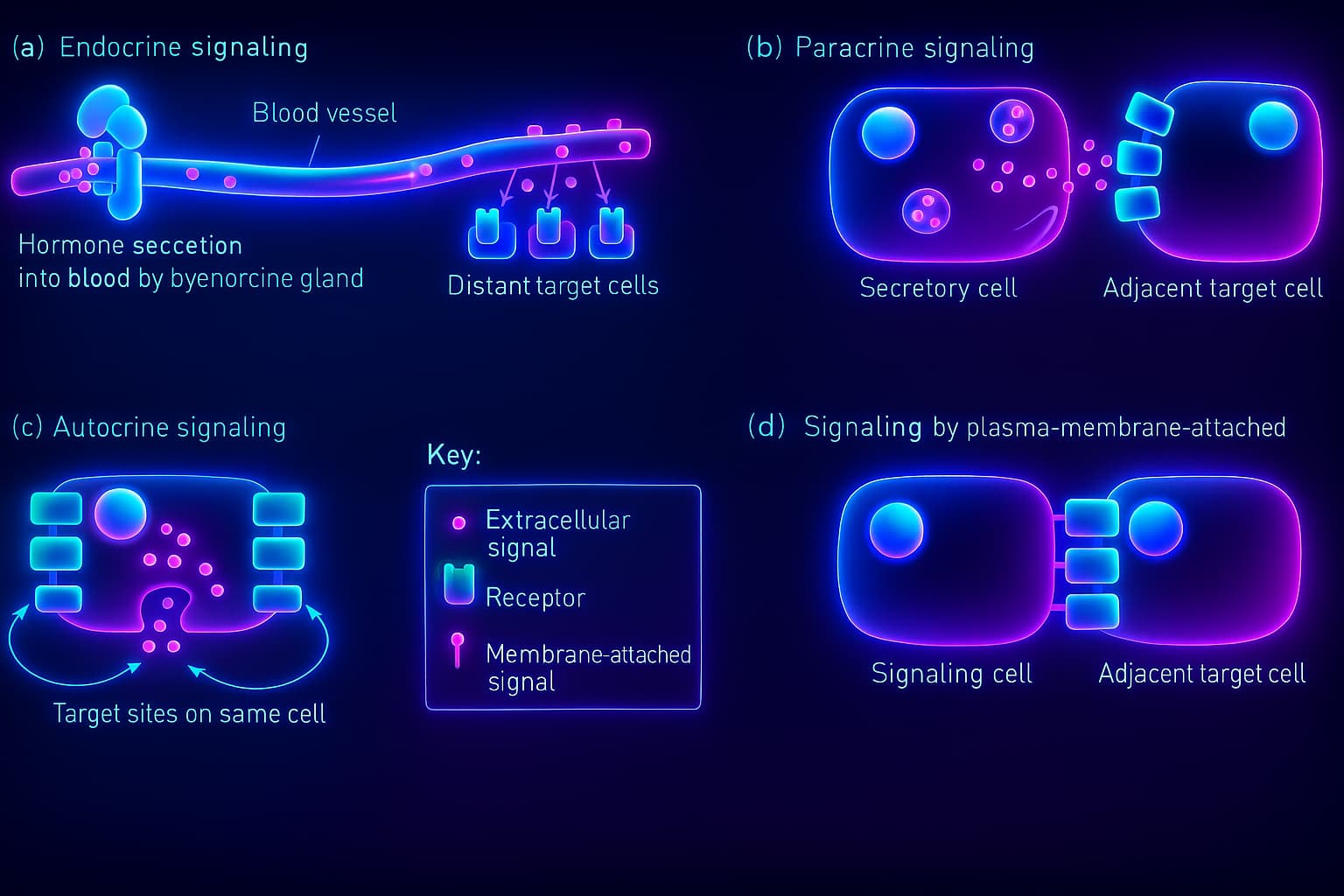
Imagine running a massive city without phones, radios, or traffic signals. Chaos, right? Now imagine your body composed of trillions of cells across countless tissues trying to function without a constant stream of biochemical messages. That’s what intercellular communication is: the language of life, spoken molecule by molecule between cells.
At every moment, your cells are sending and receiving messages, adjusting behavior based on context, environment, and need.
Vast, flexible signaling network coordinates nearly every biological process:
Without this orchestration, tissues would act independently growing out of control, ignoring damage, or failing to mount a defense. Coordination is everything. And that’s exactly what cell-to-cell signaling makes possible.
So What Are The Main Modes of Cellular Conversation?
There are several main “languages” cells use to communicate:
Together, these systems keep your cells in constant dialogue, updating each other in real time. In youth, this intercellular communication works like a tightly synchronized symphony: fast, clear, and harmonized.
But with age, this system begins to unravel. Messages are sent at the wrong time, misinterpreted, or ignored altogether. Some cells go silent. Others begin screaming inflammatory nonsense.
This slow deterioration is known as altered intercellular communication, and it’s one of the fundamental hallmarks of aging. As the system breaks down, cells lose their ability to coordinate. The result is a biological version of mass miscommunication, where metabolic control, immune precision, and tissue repair all suffer.
So we know that intercellular communication is essential, a beautifully choreographed system that keeps your cells talking, your organs cooperating, and your immune system balanced. But what causes this system to fall apart over time? Why do messages that once flowed clearly now sound like static?
Let’s zoom in on the biological culprits behind altered intercellular communication and why aging gradually scrambles the cellular conversation.
What goes wrong in the body’s communication network?
1. DNA Damage Corrupts the Message
Decades of cell division, Toxins, UV light and Telomeres shortening lead to DNA alterations especially in genes that encode hormones, receptors, or signaling proteins. The result? Disrupted cellular messages in aging. A repair signal might arrive too late, or an inflammatory alert might be sent with no threat at all, seeding confusion that spreads from cell to cell.
2. Senescent Cells Flood the Network
Senescent cells don’t divide, but they don’t stay silent either. They spew inflammatory molecules known as SASP, overwhelming normal signaling. This chronic inflammatory communication accelerates nearby aging and slows down regeneration, a major reason why inflammatory communication and longevity are so tightly linked.
3. Cells Stop Listening
Even when signals are sent clearly, aging cells may no longer respond. Their receptors become less sensitive, as seen in insulin resistance, where glucose regulation fails despite insulin being present. It’s a classic symptom of aging and intercellular signaling breakdown: messages aren’t just misdelivered… they’re ignored.
4. Chronic Inflammation Drowns Out Signals
Aging tissues live in a storm of inflammaging: constant low-grade inflammation that acts like static across the communication system. These distress signals interfere with everything from immune responses to metabolism, trapping cells in a loop of disrupted communication and degeneration.
5. Structural Breakdown in the Matrix
The extracellular matrix (ECM), the scaffold between cells, is essential for local coordination. But with age, it becomes stiff and fragmented, distorting mechanical and biochemical cues. Even helpful messages get lost in this noisy, crumbling environment.
6. Mitochondria Send False Alarms
As mitochondria age, they release damage signals (DAMPs) that mimic danger AS PART OF THE mitochondrial dysfunction. These internal false alarms ignite unnecessary inflammation, adding to the chaos of altered intercellular communication, especially in high-energy organs like the brain and muscles.
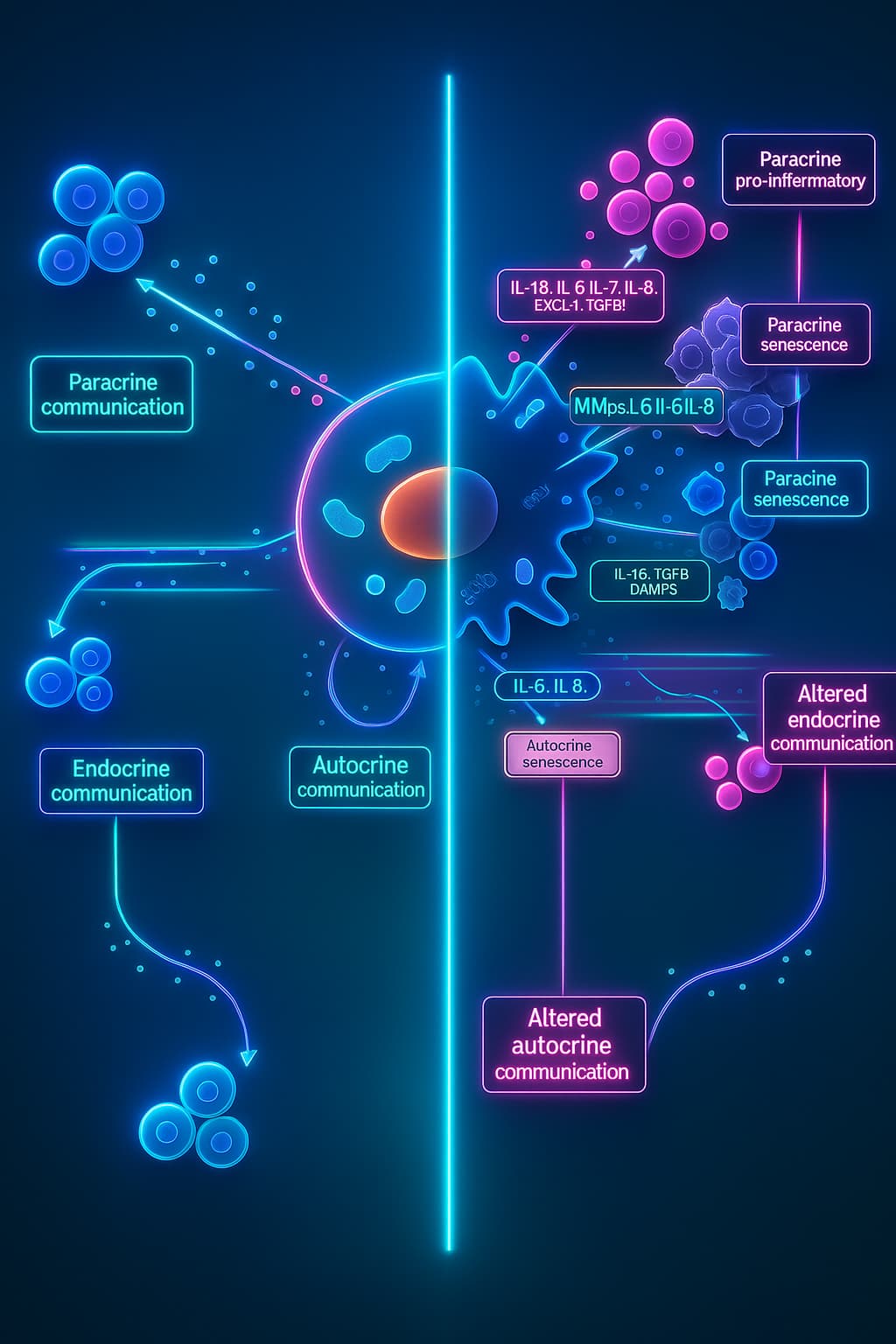
The Bottom Line
The collapse of cell-to-cell signaling in aging is layered and self-reinforcing. Mutations, inflammation, receptor loss, senescence, and mitochondrial dysfunction all feed into the breakdown, creating a tangled network of disrupted cellular messages in aging.
And when communication fails, even the healthiest cells lose their way.
Now that we’ve seen why communication breaks down with age, from DNA damage to chronic inflammation, let’s explore what this actually looks like inside an aging body.
Aging doesn’t mute the conversation between cells; it scrambles it. Cells start sending the wrong messages, ignoring the right ones, or overreacting to harmless cues. Over time, this altered intercellular communication creates confusion across systems, driving dysfunction from within.
This growing misalignment is one of the clearest signs of cell-to-cell signaling and aging in action.
So what’s actually happening between the cells
1. Inflammation Becomes the Background Noise
In youth, inflammation is an emergency response. In aging, it becomes the soundtrack.
Senescent cells, mitochondrial distress signals, and chronic immune activation all feed into an inflammatory storm. Cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-α are released nonstop, triggering inflammatory communication that disrupts tissue repair and metabolic balance.
This chronic signaling is a major reason for the observed link between inflammatory communication and longevity decline.
2. Immune Cells Lose Their Compass
The immune system relies on coordination but aging scrambles the map.
Some immune cells slow down, others become hyperactive. Senescent immune cells leak toxic signals, and SASP amplifies the confusion. The outcome? Misfires, chronic inflammation, and rising autoimmunity.
It’s a classic case of disrupted cellular messages in aging, where defense turns into self-sabotage.
3. Hormonal Signals Go Off Script
Hormones like insulin, cortisol, and estrogen are vital for long-range cell-to-cell signaling but aging throws off their rhythm.
Even when hormones are present, aged cells often don’t respond, reinforcing aging and intercellular signaling breakdown at every level.
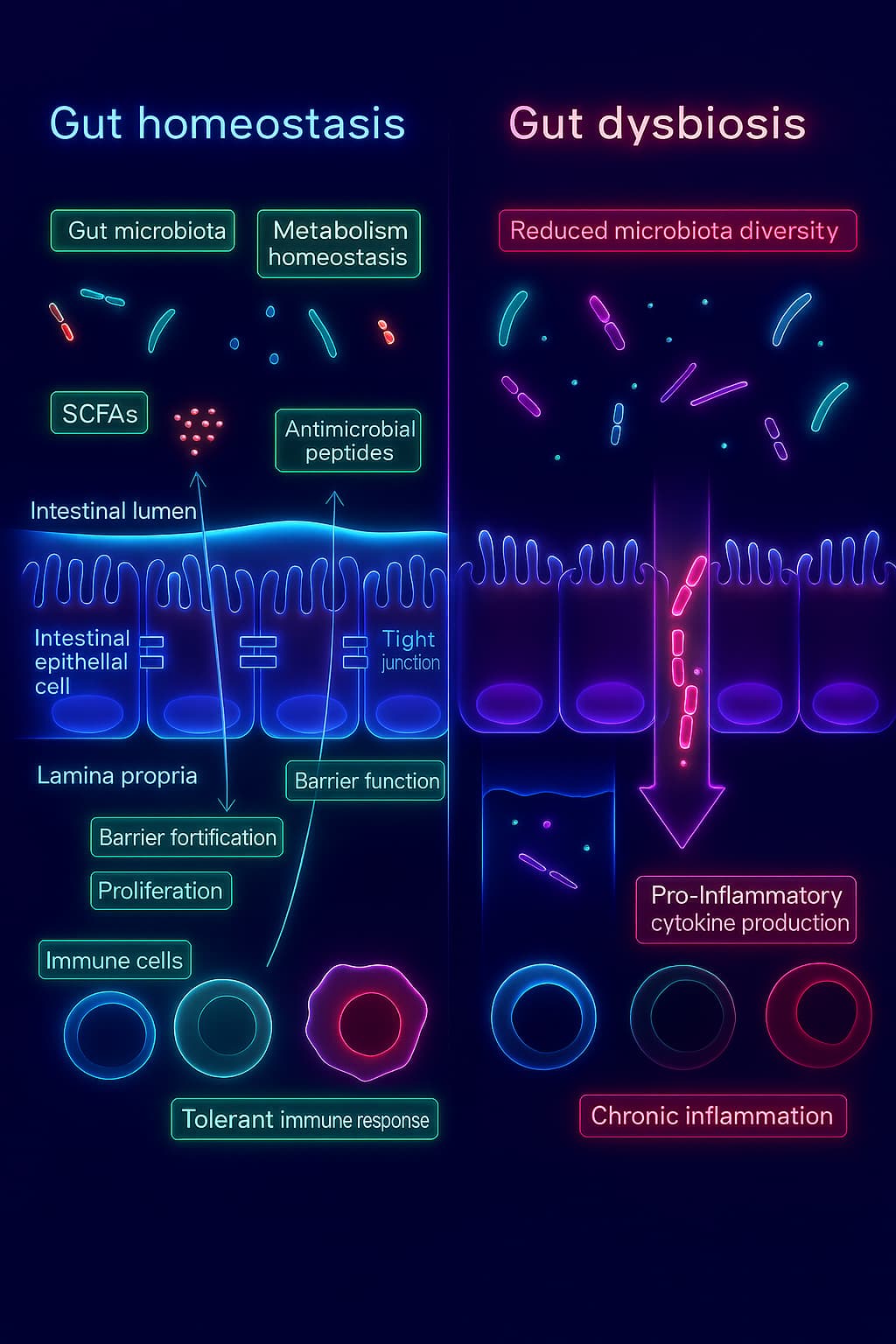
4. The Microbiome Adds to the Confusion
Your gut microbes influence immunity, mood, and metabolism. But with age, microbial diversity shrinks, the gut barrier weakens, and inflammatory compounds leak into the bloodstream.
The result? More altered intercellular communication between the gut, brain, and immune system. leading to fatigue, brain fog, and systemic inflammation.
This microbial imbalance (known as dysbiosis) quietly accelerates aging from the inside out. It fuels chronic inflammation, disrupts nutrient absorption, and weakens your body’s ability to bounce back from stress.
Over time, even your cellular signaling pathways become scrambled, adding to the noise and confusion of the aging process.
When intercellular communication starts to break down, the consequences don’t stay contained. They cascade, spreading dysfunction across organs and systems.
Why? Because your body runs on connection. Your gut talks to your brain. Your hormones regulate stress, sleep, and metabolism. Immune cells coordinate with neurons and stem cells. But when this communication network glitches, the system loses its rhythm and aging speeds up.
This is the real cost of altered intercellular communication: not just isolated problems, but a ripple of decline driven by broken messaging.
How disrupted cellular messages in aging manifest across the body?
Metabolic Dysfunction
When insulin and leptin signals go fuzzy, cells stop responding leading to high blood sugar, fat accumulation, and energy crashes. This is cell-to-cell signaling and aging at work, driving diseases like type 2 diabetes and fatty liver.
Add in chronic inflammation from fat tissue, and you get a perfect storm of inflammatory communication, metabolic confusion, and early decline.
Cognitive Decline and Brain Aging
The brain thrives on precise, rapid signaling. But with age, inflammation rises, microglia go rogue, and the blood-brain barrier weakens.
This breakdown in aging and intercellular signaling causes memory loss, slower thinking, and greater dementia risk. Gut microbes also join the chaos contributing to even more altered intercellular communication through the gut-brain axis.
Immune System Misfires
A well-coordinated immune system protects without overreacting. But aging disrupts that balance.
Some threats go unnoticed. Others provoke overkill. Senescent immune cells release toxic signals, further fueling inflammatory communication and longevity decline.
This leads to autoimmunity, chronic infections, and poor vaccine response all symptoms of disrupted cellular messages in aging.
Poor Tissue Repair and Breakdown
Cuts, strains, and inflammation rely on precise communication between stem cells, immune cells, and structural cells to heal.
But with intercellular signaling breakdown, messages arrive late or not at all. Growth factors are misdirected. Inflammation overstays its welcome. Result: slow healing, fragile skin, shrinking muscle, and weaker joints.
This is how aging and intercellular signaling breakdown undermines structural integrity at every level.
The Bottom Line
This isn’t just wear and tear. it’s a breakdown in biological coordination. A failing command center sending mixed signals across the network.
At the root of many age-related conditions: Alzheimer’s, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, autoimmunity lies altered intercellular communication. Unless we restore clarity to these signals, even the healthiest cells will falter in a storm of noise.
But if we can clean up the messages by calming inflammation, improving receptor function, and rewiring how cells talk we don’t just slow aging.
We reset the system.
Here’s the good news: while altered intercellular communication is a hallmark of aging, it’s not irreversible.
We may not be able to reset the body entirely, but we can quiet the noise, amplify the right signals, and help our cells speak clearly again. Supporting cell-to-cell signaling is one of the most effective ways to slow, and even reverse, age-related decline.
Let’s look at science-backed ways to restore the cellular conversation:
1. Eat to Reduce Inflammation
A diet rich in polyphenols (like turmeric, green tea, and berries), omega-3s, and fiber helps suppress inflammatory pathways like NF-κB, reducing inflammatory communication and supporting long-term longevity.
2. Exercise Sharpens Cellular Signals
Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, activates beneficial hormones, and clears senescent cells. This boosts signal precision and calms disrupted cellular messages in aging.
3. Sleep Repairs the Network
Sleep is when your body clears out cellular debris, resets hormonal rhythms, and reduces inflammatory load. Poor sleep leads to misfired signals and intercellular signaling breakdown.
4. Fasting Cleans Up Cellular Static
Intermittent fasting activates autophagy, improves metabolic signaling, and helps cells respond more accurately, restoring clarity to altered intercellular communication.
1. Fisetin + Quercetin
Natural senolytics that help eliminate senescent cells and reduce SASP, cleaning up toxic noise from inflammatory communication.
2. Omega-3s (EPA/DHA)
These fats improve membrane fluidity and lower inflammation, supporting healthy cell-to-cell signaling across the brain, immune system, and metabolism.
3. Probiotics + Prebiotics
A strong microbiome produces neurotransmitters and immune signals that influence the gut-brain-immune axis, a major pathway impacted by aging and intercellular signaling breakdown.
4. Curcumin + Resveratrol
These polyphenols reduce oxidative stress and calm pro-inflammatory signaling, helping restore smooth intercellular communication across multiple tissues.
When you support the body’s messaging system through food, movement, sleep, and targeted supplements you don’t just slow aging.
You give your cells their voice back.
Not medical advice. Always check with your doctor before using any supplement.
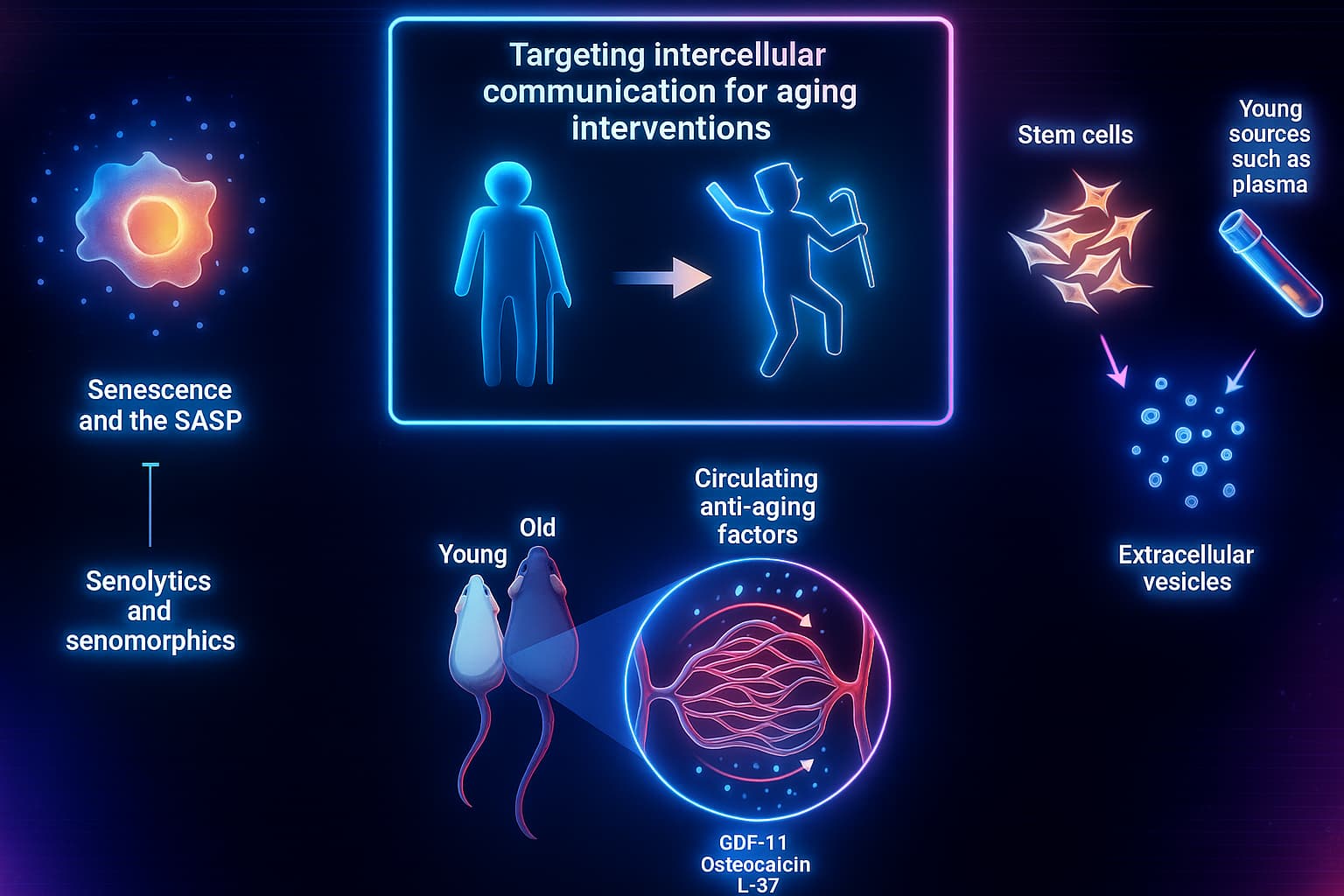
While lifestyle and supplements can help clear the static, scientists are going one step further, developing therapies that reprogram how cells talk. Think of it as upgrading the operating system behind your body’s entire communication network.
Here are a few exciting breakthroughs in the pipeline:
Senolytics: Cleaning Up the Loudest Room
Senescent cells are like cranky retirees shouting nonsense through the intercom. They don’t divide, but they do disrupt, flooding tissues with inflammatory communication and accelerating aging.
Senolytic drugs (like fisetin, dasatinib, or navitoclax) act like cellular eviction notices, targeting and clearing these noisy cells. The result? Less inflammatory chatter, more space for healthy cells, and a clearer intercellular signaling landscape.
Exosome Therapy: The Body’s Tiny Mail Carriers
Exosomes are nano-sized vesicles that cells use to send molecular messages, like tiny FedEx trucks loaded with proteins, RNAs, and lipids.
With age, the quality and quantity of these messages decline. But scientists are developing therapies that engineer or deliver rejuvenating exosomes, restoring clean, youthful communication between cells. Imagine rewriting the memo in a way aging cells can actually read.
Gene Therapy: Reprogramming the Cellular Conversation
Some therapies aim to go deeper, directly editing or enhancing genes that control cell-to-cell signaling. These include tools like CRISPR, which can flip genetic switches to restore lost sensitivity or dampen overactive inflammatory responses.
For example, boosting the expression of telomerase or FOXO3 can improve stress resilience and delay signaling breakdown. It’s like updating the factory software so cells stop misfiring and start collaborating again.
The Takeaway?
We’re heading into a future where altered intercellular communication isn’t just observed, it’s repaired. From senolytics to exosomes to gene-editing, scientists are building tools that restore harmony to the body’s cellular conversation.
And when the messages flow clearly, so does health, energy, and longevit
Aging isn’t just about decline, it’s about miscommunication.
As we get older, the elegant cellular symphony that once kept our bodies in sync begins to fall out of tune. Messages between cells get garbled. Signals are missed, delayed, or misinterpreted. This breakdown, known as altered intercellular communication, is a core hallmark of aging and one of the most important to understand.
From cell-to-cell signaling and aging to the flood of inflammatory communication driven by senescent cells, the consequences ripple across every system: cognitive decline, metabolic disorders, poor tissue repair, and immune dysfunction. These are not isolated problems, they’re symptoms of disrupted cellular messages in aging.
But here’s the hopeful part: we can do something about it.
Through anti-inflammatory nutrition, regular movement, quality sleep, and smart fasting strategies, we can restore the rhythm of healthy intercellular communication. Supplements like fisetin, omega-3s, and probiotics offer added support, and emerging therapies, from senolytics to exosome and gene-based treatments are being developed to clean up the cellular airwaves at the source.
Because when aging and intercellular signaling breakdown are addressed, the whole system works better.
So here’s to keeping the messages clear, the conversations flowing, and every cell in your body tuned to the same healthy frequency for longer, stronger, more vibrant years ahead.
So let’s keep the messages clear and the conversation going.
Now that you’ve unlocked the science behind Altered intercellular communication, why stop here? The aging process is a mosaic and altered intercellular communication is just one piece.
Explore the other hallmarks of aging and see how they connect, interact, and build the bigger picture of biological aging and longevity. Pick the ones that spark your curiosity:
Each of these threads tells a different part of the aging story and each one offers a chance to intervene, repair, and thrive longer.
So… which one will you explore next?